The Ethics of Generative AI in Supply Chain Operations: Principles and Practices
Generative AI, a subset of artificial intelligence, is rapidly transforming various industries. Its ability to create new content, from text and images to music and code, is poised to revolutionize how we work and live. This innovative technology leverages complex algorithms to learn patterns from vast datasets, enabling it to generate novel outputs that mimic human creativity.
Key Applications of Generative AI
The potential applications of generative AI span a wide range of sectors. From generating marketing materials and customer support responses to creating realistic images and 3D models, its practical uses are constantly evolving. Imagine generating personalized educational materials tailored to individual student needs, or creating realistic simulations for scientific research.
Generative AI models are also being used to enhance creative processes, helping artists, writers, and musicians explore new ideas and push creative boundaries. This opens up exciting opportunities for innovation in various fields.
Underlying Principles of Generative AI Models
At the heart of generative AI lie sophisticated machine learning algorithms. These models are trained on massive datasets to identify patterns and relationships within the data. Once trained, they can generate new data points that adhere to the learned patterns, producing outputs similar to the examples they were trained on.
Deep learning models, such as neural networks, are frequently employed in generative AI. These networks can learn complex representations of data, enabling them to generate outputs with high levels of realism and sophistication.
The Role of Data in Generative AI
The quality of the data used to train generative AI models significantly impacts the quality of the generated output. High-quality, diverse, and representative datasets are crucial for ensuring that the models learn accurate and nuanced representations of the underlying phenomena. Poor or biased datasets can lead to flawed or discriminatory outputs.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
The rapid advancement of generative AI raises crucial ethical considerations. Issues such as copyright infringement, misinformation, and the potential for misuse need careful consideration and proactive solutions. The development and deployment of generative AI should be guided by ethical principles and regulations to ensure responsible innovation.
Future Trends and Implications
The future of generative AI is filled with exciting possibilities and potential challenges. Continued advancements in algorithms, data availability, and computational power promise further improvements in the quality and creativity of generated content. This technology has the potential to reshape industries, create new jobs, and address complex societal challenges. However, careful consideration of the ethical implications and potential risks is crucial for responsible implementation.
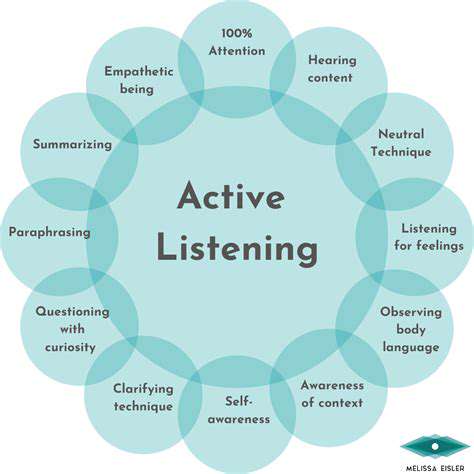
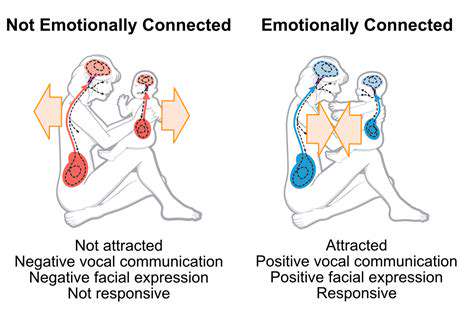
Empathy is a crucial component of effective communication and interpersonal relationships. It involves the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person. When we approach interactions with empathy, we acknowledge the emotional landscape of those around us, fostering a deeper connection and understanding. This ability to see things from another's perspective is vital in resolving conflicts and building strong, healthy relationships. Empathy allows us to connect on a human level, creating a more supportive and harmonious environment.

Human-AI Collaboration and Workforce Adaptation
Human-AI Collaboration in the Workplace: A New Era
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into the workplace is rapidly transforming how we work. This shift is not simply about replacing human workers; instead, it's about a fundamental reimagining of the workforce, with AI becoming a powerful tool for augmenting human capabilities and driving innovation. This new paradigm necessitates a careful consideration of how humans and AI can collaborate effectively to maximize productivity and create a more fulfilling work experience.
The Impact of AI on Various Job Roles
AI's influence extends across a broad spectrum of professions, from data analysis and customer service to creative fields like design and writing. AI systems can automate routine tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on higher-level strategic thinking and problem-solving. This shift requires workers to adapt and acquire new skills in order to effectively collaborate with AI tools. For example, in the medical field, AI can assist doctors in diagnosing diseases and personalizing treatment plans, allowing doctors to focus on the patient's overall well-being.
Skills Needed for the AI-Powered Workplace
To thrive in the AI-driven future of work, employees need to develop a diverse skillset encompassing technical proficiency, critical thinking, and creative problem-solving. A strong foundation in data literacy, digital literacy, and the ability to understand and interpret AI outputs is crucial. These skills will be essential for effectively utilizing AI tools and navigating the complexities of human-AI collaboration.
Ethical Considerations in AI Integration
The integration of AI into the workplace also raises important ethical considerations. Bias in algorithms, data security, and the potential displacement of workers are critical issues that must be addressed proactively. A thoughtful and ethical approach to AI development and implementation is crucial to ensure responsible and equitable outcomes for all stakeholders.
The Future of Work: Adapting to Change
The evolution of work is not without its challenges. Adapting to the rapidly changing landscape necessitates continuous learning and skill development. Workers need to be prepared to embrace new technologies and adapt to evolving job roles. This requires a proactive approach to upskilling and reskilling initiatives, ensuring that the workforce remains competitive and relevant in the face of technological advancements.
Collaboration Strategies for Human-AI Teams
Effective collaboration between humans and AI requires carefully designed strategies and protocols. Clear communication channels, well-defined roles and responsibilities, and robust training programs are essential to ensure that both humans and AI are operating harmoniously within a team. This integration necessitates a shift from viewing AI as a replacement to acknowledging it as a powerful tool that can enhance human capabilities.
Addressing Concerns about Job Displacement
One of the most prevalent concerns surrounding AI integration is the potential for job displacement. While some jobs may become automated, many new opportunities will emerge in areas related to AI development, implementation, and management. Investing in education and training programs that prepare workers for the evolving job market is crucial to mitigate potential negative impacts. It's imperative to focus on reskilling and upskilling initiatives to ensure a smooth transition for all workers affected by technological advancement.