Digital Twin for Automated Decision Making in Supply Chain Operations
Automated Decision-Making: Implementing AI and Machine Learning
Automated Decision-Making Systems
Automated decision-making systems are rapidly evolving, impacting various sectors from finance to healthcare. These systems leverage algorithms and data to process information and make choices, often at a scale and speed impossible for humans. This automation promises increased efficiency and objectivity in many processes.
Understanding the underlying algorithms is crucial for evaluating the fairness and reliability of these systems. Often, complex algorithms, especially deep learning models, operate as black boxes, making it difficult to understand the logic behind their decisions. This lack of transparency can lead to unforeseen biases and errors.
Implementation Challenges
Implementing automated decision-making systems presents significant challenges. Data quality is paramount; inaccurate, incomplete, or biased data can lead to flawed decisions and potentially discriminatory outcomes. Ensuring data privacy and security is also critical, as these systems often handle sensitive personal information.
A robust evaluation process is essential to identify and mitigate potential risks. Rigorous testing and validation are needed to ensure the system performs as intended across a wide range of scenarios and conditions. Furthermore, ongoing monitoring and adjustments are needed to adapt to evolving circumstances and maintain accuracy.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical implications of automated decision-making are substantial. Decisions made by machines can have profound consequences for individuals and society as a whole. Bias in the data or algorithms can perpetuate existing societal inequalities, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Careful consideration must be given to the potential for these systems to exacerbate existing social divides.
Transparency and accountability are vital in this context. Understanding how the system arrived at a particular decision is essential for trust and for identifying potential errors or biases. Clear guidelines and regulations are needed to ensure ethical and responsible implementation of these systems.
Future Trends and Opportunities
The future of automated decision-making holds significant promise, particularly in areas like personalized medicine and customized learning. These systems could revolutionize how we approach complex problems and optimize processes in a variety of industries. The potential for innovation and efficiency gains is enormous.
However, the development and deployment of these systems must be carefully managed to avoid unintended consequences. Collaboration between technologists, ethicists, and policymakers is essential to ensure that these powerful tools are used responsibly and equitably. This will ensure that automation enhances rather than undermines human well-being.
Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience and Adaptability

Building a Robust Supply Chain
A resilient supply chain is crucial for businesses to navigate unforeseen disruptions and maintain operational stability. Developing a robust supply chain involves a proactive approach to identifying potential vulnerabilities and implementing strategies to mitigate them. This includes diversification of suppliers, geographically dispersed manufacturing facilities, and strong inventory management systems. These strategies help reduce reliance on single points of failure and ensure continuity of operations even in times of crisis, such as natural disasters or economic downturns. Establishing clear communication channels and strong relationships with suppliers is also paramount, allowing for rapid response and adaptation to changing conditions.
Supply chain resilience isn't a one-time project, but rather an ongoing process of continuous improvement. Regular audits and assessments of the supply chain are essential for identifying weaknesses and implementing necessary adjustments. This includes evaluating supplier performance, analyzing logistics routes, and assessing risk factors. A proactive approach to risk management, incorporating scenario planning and contingency strategies, will further enhance the ability to respond effectively to potential disruptions.
Diversifying Supplier Networks
Reducing reliance on a single supplier is a vital component of building a resilient supply chain. Diversifying the supplier network spreads risk across multiple sources, preventing a single disruption from crippling the entire operation. This strategy not only enhances business continuity but also offers greater flexibility in sourcing materials and negotiating favorable contracts. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers allows for greater negotiation power and ensures a wider range of options for sourcing materials.
By working with diverse suppliers, businesses can gain access to a wider range of expertise and capabilities. This can lead to improved product quality, faster delivery times, and potentially lower costs. Diversifying suppliers also promotes a more sustainable supply chain by supporting a wider range of businesses and communities.
Implementing Advanced Technology
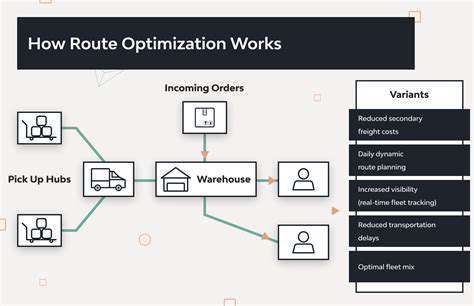
Integrating advanced technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) can significantly enhance supply chain visibility and responsiveness. These technologies offer real-time tracking of goods, enabling businesses to monitor shipments, predict potential delays, and make informed decisions about resource allocation. By leveraging data analytics, businesses can identify patterns and trends in supply chain performance, allowing for proactive interventions and optimized processes.
Implementing robust inventory management systems can help minimize disruptions. Real-time inventory tracking allows businesses to anticipate demand fluctuations and adjust production and procurement accordingly. Automated systems can also optimize warehousing and distribution processes, improving efficiency and reducing costs. Utilizing predictive analytics to forecast future demand allows for proactive inventory management and reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
Strengthening Communication and Collaboration
Transparent communication and strong collaboration with stakeholders across the supply chain are crucial for building resilience. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers, distributors, and customers enables timely information sharing and rapid response to emerging issues. Open communication fosters trust and allows for collaborative problem-solving in the face of challenges.
Fostering strong relationships with key stakeholders is essential. This includes regular communication, joint planning, and mutual support during times of difficulty. This collaborative approach promotes a shared understanding of risks and opportunities, empowering businesses to work together to build a more resilient and adaptable supply chain. This collaboration extends beyond internal teams to include external partners, fostering a network of support throughout the entire supply chain.
Read more about Digital Twin for Automated Decision Making in Supply Chain Operations
Hot Recommendations
- Digital Twin for Automated Decision Making in Supply Chain Operations
- 5G for high definition video streaming for remote inspections
- Generative AI for Automated Freight Negotiations: Smarter Deals
- Automating Supply Chain Customer Service Responses with Generative AI
- Digital Twin for Predictive Logistics Planning
- Sustainable supply chain materials sourcing
- The Strategic Importance of Advanced Robotics in Supply Chain
- The Creative Applications of Generative AI in Supply Chain Forecasting
- Data Integration Challenges in Mergers & Acquisitions for Supply Chains
- From Predictive to Prescriptive: The Evolution of Supply Chain Analytics