Blockchain for ethical sourcing of raw materials
Blockchain's Potential for Transparency and Traceability
Improving Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology introduces a groundbreaking method for managing supply chains, providing unparalleled transparency and traceability. By documenting every transaction on a distributed ledger, businesses can monitor products from their origin to the end consumer, removing intermediaries and establishing a more reliable and verifiable process. This enhanced visibility fosters accountability, allowing consumers to make informed decisions about their purchases and building greater trust in the supply chain. This transparency enables businesses to swiftly identify and resolve issues, minimizing disruptions and ensuring ethical sourcing.
Enhancing Ethical Sourcing Practices
Blockchain offers significant advantages for ethical sourcing by verifying the origin and production methods of goods. By documenting details such as labor conditions, environmental impact, and adherence to ethical standards, businesses can meticulously track raw materials and finished products, ensuring ethical standards are upheld throughout the process. This detailed record-keeping promotes accountability, allowing businesses to quickly address any ethical concerns. The immutable nature of blockchain provides a tamper-proof record, protecting against fraud and enabling consumers to trust product origins and production methods.
Promoting Accountability and Responsibility
Blockchain's inherent transparency fosters accountability and responsibility across the supply chain. By maintaining a shared, auditable record of transactions, blockchain empowers stakeholders to hold each other accountable for ethical and sustainable practices. This shared record allows all supply chain participants to verify product legitimacy and integrity, deterring fraudulent activities and promoting responsible behavior. Transparency and accountability are essential for ethical sourcing, and blockchain technology plays a pivotal role in achieving these goals.
Facilitating Traceability in the Food Industry
The food industry stands to benefit significantly from blockchain's traceability capabilities. By tracking food products from farm to table, blockchain technology ensures food safety, detects contamination swiftly, and prevents foodborne illnesses. This detailed record-keeping also helps establish the origin and authenticity of ingredients, combating food fraud and ensuring consumer confidence. The ability to trace every step in the production process strengthens the system for maintaining food quality and safety.
Strengthening Consumer Confidence
Blockchain's transparency and traceability bolster consumer confidence in ethical sourcing initiatives. Knowing that products are sourced ethically and sustainably empowers consumers to make informed choices. By providing verifiable information about product origins, production methods, and environmental impact, blockchain equips consumers to support businesses that adhere to ethical standards. This increased transparency builds trust between businesses and consumers, driving the adoption of ethical sourcing practices and fostering a more sustainable marketplace.
Implementing Blockchain Solutions for Ethical Sourcing
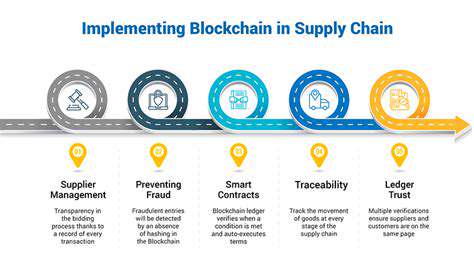
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that records and verifies transactions across multiple computers. This distributed nature eliminates the need for a central authority, enhancing security and transparency. The ledger is replicated across a network of participants, ensuring data immutability and reliability.
Understanding cryptographic principles is essential to grasping blockchain's power. Cryptography ensures transaction security and integrity by encrypting and verifying data. This cryptographic hashing method creates a unique fingerprint for each block, making tampering virtually impossible.
Choosing the Right Blockchain Platform
Selecting the appropriate blockchain platform is crucial for project success. Different platforms offer varying functionalities, such as scalability, security features, and developer support. Factors like intended use case, transaction volume, and budget should guide the selection process.
Evaluating platform strengths is critical. Some prioritize speed, while others focus on security and privacy. Careful consideration of these differences ensures the chosen platform aligns with project goals.
Developing a Secure Blockchain Application
Developing secure blockchain applications requires meticulous attention to detail and a deep understanding of cryptographic principles. Smart contract design and implementation are crucial, as they automate processes and represent the application's core logic. Ensuring smart contract security is paramount to prevent vulnerabilities and financial losses.
Implementing robust security measures is essential to protect against threats. This includes using strong cryptographic algorithms, conducting regular security audits, and adhering to best practices throughout development. A proactive approach to security prevents unauthorized access and data breaches.
Implementing Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with terms written into code and stored on a blockchain, ensuring transparency and immutability. Understanding the programming language and framework of the chosen blockchain platform is vital for successful implementation.
Thorough testing and debugging are essential to minimize errors and ensure contract functionality. Ensuring contract accuracy and functionality is crucial for successful blockchain application deployment.
Deploying and Maintaining the Solution
Deploying a blockchain solution involves integrating it with existing systems and ensuring seamless data flow. This requires careful configuration and testing to ensure compatibility and performance. Thorough testing before deployment identifies and addresses potential issues.
Ongoing maintenance is vital for long-term viability. This includes monitoring system performance, handling updates, and addressing security vulnerabilities. Regular maintenance ensures the stability and security of the blockchain solution.
The Future of Ethical Sourcing with Blockchain

Ethical Sourcing in a Globalized World
The interconnectedness of global supply chains necessitates a focus on ethical sourcing practices. Companies face scrutiny from consumers and investors demanding transparency and accountability. This pressure drives businesses to address labor rights, environmental sustainability, and fair trade practices proactively.
Ethical sourcing fosters trust and loyalty through fair wages, safe working conditions, and human rights protection. This approach builds strong supplier relationships and enhances brand reputation.
Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Implementing systems for supply chain transparency and traceability is essential. Understanding material origins, product journeys, and working conditions at each stage is vital. Technologies like blockchain and GPS tracking enhance visibility and accountability.
Labor Rights and Fair Wages
Prioritizing labor rights and ensuring fair wages is crucial. This includes respecting freedom of association, ensuring safe working conditions, and providing living wages. Companies must monitor supplier practices to ensure compliance.
Fostering a culture of respect and dignity within the supply chain empowers workers and builds a sustainable future.
Environmental Sustainability and Resource Management
Environmental impact is increasingly important. Companies must consider resource use, waste reduction, and emission minimization in their supply chains. Sustainable sourcing strategies, such as recycled materials and renewable energy, mitigate environmental footprints.
Technology's Role in Ethical Sourcing
Technology revolutionizes ethical sourcing by providing insights into supply chains and enabling real-time monitoring. Advanced data analytics and mobile reporting systems identify risks and opportunities for improvement.
Continuous supply chain monitoring ensures ethical standards are maintained.
The Future of Ethical Sourcing Initiatives
The future of ethical sourcing relies on collaboration and continuous improvement. Sharing best practices, fostering industry standards, and supporting ethical initiatives are crucial. Strong partnerships between companies, NGOs, and governments drive meaningful change.
Embracing technology, prioritizing worker rights, and promoting environmental responsibility pave the way for an equitable and sustainable future. Ethical sourcing becomes a fundamental part of business strategy.
Read more about Blockchain for ethical sourcing of raw materials
Hot Recommendations
- Beyond Buzzwords: Real World Applications of Supply Chain Tech
- Digital twin for simulating human robot collaboration scenarios
- The Future of Supply Chain Strategy Development: AI Driven
- Big Data in Supply Chain: Challenges and Opportunities
- Generative AI for Supply Chain Workforce Augmentation
- Simulating the Impact of Supplier Disruptions with Digital Twins
- Sustainable urban logistics planning and policy
- Overcoming Data Fragmentation in Global and Multi Enterprise Supply Chains
- Robotics for cross docking operations: Speeding transit
- Natural language generation for automated weekly supply chain reports