The Impact of Blockchain on Supply Chain Dispute Resolution
Mediation provides a structured environment for parties in conflict to communicate and find common ground. A neutral third party, the mediator, facilitates discussions and assists in identifying potential solutions. This approach emphasizes cooperation and often leads to more amicable resolutions compared to adversarial methods like litigation. Mediation can be particularly valuable when preserving relationships between parties is crucial.
Arbitration: A Binding Decision-Making Process
Arbitration involves a neutral third party, the arbitrator, who hears evidence and arguments from both sides of the dispute. The arbitrator then makes a binding decision that the parties must abide by. This approach offers a more formal and structured process than negotiation or mediation, and it can be faster and more efficient than litigation. Arbitration is frequently used in complex supply chain disputes where a quick, decisive resolution is needed.
Limitations of Traditional Methods in Modern Supply Chains
While traditional dispute resolution methods have served the supply chain well, they may not be entirely sufficient in today's complex and globalized supply chains. The increasing interconnectedness and complexity of modern supply chains, along with the use of sophisticated technology, introduce new challenges and require innovative approaches to dispute resolution. Globalization itself presents unique challenges in terms of jurisdiction and legal frameworks, impacting dispute resolution options.
Blockchain's Role in Enhancing Transparency and Traceability

Blockchain's Impact on Transparency
Blockchain technology fundamentally alters the landscape of transparency by creating a shared, immutable ledger of transactions. This shared record, accessible to all participants, eliminates the need for intermediaries and significantly reduces the potential for fraud and manipulation. This inherent transparency fosters trust among stakeholders, a crucial element in any successful business or societal system. By providing a verifiable record of every transaction, blockchain enhances accountability and builds confidence in the integrity of the process.
The transparency afforded by blockchain extends beyond financial transactions. In supply chain management, for instance, every step in the journey of a product, from origin to consumer, can be tracked. This granular level of visibility allows businesses to identify and address inefficiencies, improve quality control, and ultimately build greater consumer trust in the provenance of goods. Real-time data accessibility also empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions and enhance overall process efficiency.
Improving Efficiency and Speed
One of the most significant advantages of blockchain technology is its potential to streamline processes and accelerate transactions. By eliminating intermediaries and automating verification steps, blockchain transactions can be completed significantly faster than traditional methods. This speed and efficiency translate into substantial cost savings for businesses, particularly those involved in international trade or financial transactions.
Enhancing Security and Trust
Blockchain's decentralized nature contributes to its robust security. The distributed ledger system makes it incredibly difficult for malicious actors to tamper with records, as any attempt would require coordinated efforts across a vast network of participants. The inherent cryptographic security further strengthens the system's resilience against attacks. This inherent security fosters trust, crucial for encouraging adoption and expansion in various sectors.
Security and Data Integrity
Data integrity is paramount in many industries. Blockchain's immutable nature ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, maintaining the accuracy and integrity of the data. This characteristic makes blockchain particularly well-suited for applications requiring high levels of data security and reliability, such as healthcare records or intellectual property management.
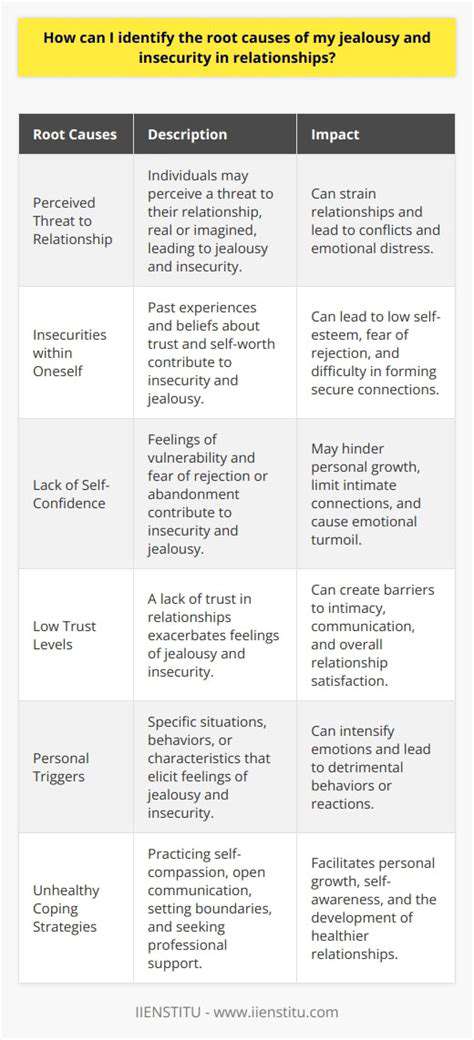
Applications in Supply Chain Management
Blockchain's ability to track products and materials throughout the supply chain offers numerous benefits. By providing a transparent and verifiable record of each stage, from origination to delivery, blockchain can enhance traceability, reduce counterfeiting, and improve overall supply chain efficiency. This transparency ensures that consumers are aware of the origin and journey of the goods they purchase, fostering accountability and trust.
Potential for Decentralization and Disruption
The decentralized nature of blockchain has the potential to disrupt traditional business models by reducing reliance on intermediaries and central authorities. This disruption can lead to greater efficiency and cost savings for businesses and consumers. Blockchain's potential also extends to areas like voting systems, where its secure and transparent nature could revolutionize democratic processes. This decentralized approach to various sectors could lead to more equitable and transparent systems.
Streamlining Dispute Resolution Processes with Smart Contracts
Improving Efficiency and Transparency
Smart contracts, by automating the execution of agreements, significantly reduce the time and resources needed for dispute resolution. Instead of lengthy legal battles, parties can rely on predefined rules and conditions to automatically determine the next steps. This automation streamlines the process, potentially cutting down on months of negotiation and legal fees. This enhanced efficiency translates directly into cost savings for all stakeholders involved, making the overall process more attractive and accessible.
Transparency is another key benefit. Smart contracts, often residing on a public blockchain, provide a transparent record of all transactions and interactions. This clear audit trail allows all parties to easily track the progress of the dispute resolution process, fostering trust and minimizing the potential for manipulation or hidden agendas. The verifiable and immutable nature of blockchain technology significantly reduces ambiguity and the risk of disputes arising from conflicting interpretations of events.
Enhancing Dispute Resolution Processes
Smart contracts can be designed to incorporate a variety of dispute resolution mechanisms, including arbitration and mediation. These mechanisms can be embedded directly into the contract's code, ensuring that the chosen process is automatically triggered when a dispute arises. This proactive approach reduces delays and ensures that the chosen resolution method is applied consistently and fairly. The pre-defined nature of smart contract dispute resolution mechanisms promotes a more predictable and controlled outcome.
Reducing Costs and Time
The automation inherent in smart contracts dramatically reduces the time and resources required for human intervention in dispute resolution. This translates directly into significant cost savings for all parties involved. By automating the execution of predefined clauses and procedures, smart contracts eliminate the need for extensive legal consultations, court hearings, and other costly interventions. This reduction in costs and time significantly lowers the overall financial burden of resolving disputes.
Promoting Fairness and Impartiality
Smart contracts, by their very nature, are designed to be impartial and transparent. The predefined rules and conditions are programmed into the contract, ensuring that all parties are treated equally and fairly. This eliminates the potential for bias or manipulation that can occur in traditional dispute resolution processes. The inherent impartiality and transparency of smart contracts foster a sense of trust and confidence among all stakeholders.
Facilitating Global Collaboration
Smart contracts can facilitate dispute resolution across geographical boundaries, enabling parties in different locations to participate effectively and efficiently. The decentralized nature of blockchain technology allows for the secure and transparent exchange of information, regardless of the parties' physical location. This seamless global collaboration enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of dispute resolution, bridging geographical barriers and promoting international cooperation.
Advanced solar technologies are rapidly evolving, offering unprecedented opportunities to harness the sun's energy for a sustainable future. These technologies go beyond the traditional photovoltaic panels, exploring innovative approaches to capture and convert solar radiation into usable energy. This exploration delves into the core principles and applications of these cutting-edge systems, promising significant advancements in renewable energy.
Improving Communication and Collaboration Among Stakeholders
Effective Communication Strategies for Stakeholders
Improving communication among stakeholders is crucial for successful project execution. Clear and concise communication channels, including regular meetings, email updates, and shared project dashboards, are vital for keeping everyone informed and aligned. These strategies foster transparency and trust, enabling stakeholders to understand their roles and responsibilities within the project lifecycle. Effective communication also allows for prompt identification and resolution of potential conflicts or roadblocks, minimizing disruptions and maximizing project efficiency. This proactive approach builds stronger relationships among stakeholders, leading to greater engagement and a more positive project environment.
Furthermore, tailoring communication styles to individual stakeholder preferences is essential. Some stakeholders may prefer detailed reports, while others might find concise summaries more effective. Actively listening to stakeholder feedback and incorporating their perspectives into communication strategies enhances engagement and fosters a sense of ownership. By creating a two-way communication flow, organizations can cultivate a collaborative environment where everyone feels heard and valued, ultimately contributing to project success.
Collaboration Tools and Technologies for Enhanced Stakeholder Engagement
Leveraging appropriate collaboration tools and technologies can significantly enhance stakeholder engagement and communication. Platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and project management software provide centralized hubs for information sharing, task assignment, and progress updates. These tools facilitate real-time communication, allowing stakeholders to easily connect, share documents, and collaborate on tasks. The ability to track progress and access relevant information within a single platform streamlines workflows and reduces the potential for misunderstandings.
Implementing video conferencing solutions allows for face-to-face interactions, fostering stronger relationships and facilitating more nuanced communication. This is particularly valuable for geographically dispersed teams or stakeholders who require a more personal connection. By providing a virtual meeting space, organizations can bridge geographical gaps and maintain a sense of community among stakeholders, regardless of their location.
Document management systems and version control tools are essential for maintaining accurate records and facilitating seamless collaboration on shared documents. This ensures that everyone has access to the latest version of a document, minimizing errors and ensuring that all stakeholders are working with the same information. These technologies promote transparency and accountability, contributing to a more efficient and effective project environment.
Utilizing project-specific wikis and knowledge bases allows stakeholders to easily access relevant information, share best practices, and contribute to the collective knowledge base of the project. This knowledge sharing fosters a culture of learning and continuous improvement, ultimately strengthening stakeholder collaboration.
By utilizing a combination of these tools, organizations can create a dynamic and collaborative environment that empowers stakeholders to effectively contribute to the project's success.
The Future of Blockchain-Enabled Dispute Resolution in Supply Chains
Decentralized Trust and Transparency
Blockchain technology fundamentally alters the nature of trust in supply chains. By recording every transaction immutably and transparently, it eliminates the need for intermediaries and fosters a shared, verifiable record of goods' journey. This decentralization minimizes the risk of fraud and manipulation, empowering all participants to verify the authenticity and origin of products, ultimately building a more trustworthy and transparent ecosystem.
This increased transparency allows for real-time tracking of goods, from origin to final destination. This detailed visibility enables stakeholders to quickly identify and address issues, reducing delays and costs associated with disputes. Furthermore, the immutable nature of blockchain records ensures that all parties have access to a definitive history of the transaction, eliminating ambiguity and facilitating dispute resolution processes.
Automated Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Smart contracts, self-executing agreements written into the blockchain, can automate many aspects of dispute resolution. Pre-defined clauses, triggered by specific events (e.g., late delivery, quality issues), can automatically initiate a dispute resolution process. This process can involve mediation, arbitration, or even simple payment adjustments, all executed without the need for lengthy and costly human intervention.
These automated mechanisms can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with resolving disputes. By streamlining the process, blockchain-enabled systems can ensure timely resolutions, minimizing disruptions to the supply chain and fostering greater efficiency. This automation drastically decreases the potential for human error and bias, leading to fairer and more equitable outcomes.
Improved Efficiency and Reduced Costs
The streamlined processes facilitated by blockchain significantly improve the efficiency of supply chain operations. Automated dispute resolution mechanisms, transparent tracking, and reduced reliance on intermediaries all contribute to a more efficient and cost-effective system. Companies can save on legal fees, administrative costs, and the time lost to protracted disputes.
These savings are not limited to the immediate financial gains. Reduced disputes lead to greater operational stability, allowing companies to focus on core business activities instead of resolving conflicts. This focus on core activities, coupled with reduced administrative costs, can lead to a significant overall improvement in productivity and profitability.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Blockchain fosters a more collaborative environment within supply chains. Shared access to the immutable ledger promotes open communication and transparency among all stakeholders. This improved communication enables proactive identification of potential issues and facilitates swift and effective solutions, minimizing the likelihood of escalated disputes. Crucially, this enhanced communication also reduces the potential for misunderstandings and misinterpretations that often fuel conflicts.
Streamlined Legal Processes
Blockchain's inherent transparency and immutability significantly streamline legal processes related to supply chain disputes. The verifiable and auditable nature of transactions on the blockchain simplifies evidence gathering, reducing the need for lengthy document reviews and legal proceedings. This efficiency translates directly into cost savings and time savings for all parties involved in the dispute resolution process.
By providing a secure and transparent platform for recording and verifying transactions, blockchain mitigates the need for complex and often costly legal procedures. This streamlined approach not only accelerates the resolution process but also reduces the risk of disputes escalating into protracted legal battles, ultimately fostering a more amicable and efficient resolution process.
The Role of Regulatory Frameworks
While blockchain offers significant advantages for dispute resolution in supply chains, clear regulatory frameworks are crucial for its effective implementation. Governments need to establish guidelines that address data privacy, security, and the legal enforceability of smart contracts. International collaboration and standardization are essential to ensure that blockchain-enabled dispute resolution systems are globally recognized and accepted. A robust legal framework is critical to ensure that the technology is utilized in a responsible and accountable manner.
The development of clear legal frameworks will provide the necessary confidence and security for businesses to adopt blockchain technology in their supply chains. This will allow for wider adoption and the realization of the full potential of blockchain-enabled dispute resolution, promoting trust and efficiency across global supply networks. Such frameworks will also need to accommodate evolving legal considerations as blockchain technology continues to evolve.