Leveraging External Data for Supply Chain Insights
The Growing Importance of External Data in Supply Chain Management
Understanding the Value of External Data
External data, encompassing a vast array of information beyond a company's internal systems, is increasingly crucial for effective supply chain management. This data, sourced from diverse sources like market research reports, weather forecasts, and social media trends, provides a comprehensive view of the external environment impacting the supply chain. By incorporating this external perspective, businesses gain a more accurate and proactive understanding of potential disruptions and opportunities, enabling them to make more informed decisions.
Enhanced Forecasting and Planning
Accurate forecasting is paramount for a resilient supply chain. External data sources, like economic indicators and historical sales data, provide valuable insights for anticipating future demand and supply fluctuations. Utilizing this data, companies can develop more precise demand forecasts, leading to optimized inventory levels, reduced stockouts, and minimized waste. This advanced planning translates directly to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Improved Risk Management Capabilities
Supply chains are inherently vulnerable to various risks, from natural disasters to geopolitical instability. External data sources can identify and assess these risks in advance, allowing businesses to implement proactive mitigation strategies. Tracking news reports, social media sentiment, and even satellite imagery can signal potential disruptions, enabling companies to adjust their operations and secure alternative suppliers or transportation routes, thereby enhancing resilience.
Real-time Visibility and Agility
Real-time data streams from external sources provide a dynamic view of the supply chain's performance. This visibility allows for swift responses to unforeseen events. For example, tracking traffic conditions, port congestion, and even social media buzz around product quality can alert companies to bottlenecks and allow for immediate adjustments, ensuring timely delivery and maintaining customer satisfaction.
Optimizing Transportation and Logistics
External data on traffic patterns, fuel prices, and even weather conditions can significantly optimize transportation and logistics. By incorporating these real-time data points, companies can make informed decisions on routing, mode selection, and carrier choice, ultimately reducing transportation costs and delivery times. This optimization directly impacts profitability and customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Customer Insights and Demand Response
Understanding customer preferences and behaviors is critical to meeting their needs. External data, including social media sentiment analysis and market research reports, allows businesses to gain valuable insights into customer demands and preferences. This knowledge can be used to customize products, tailor marketing campaigns, and respond to shifts in demand more effectively. This responsiveness directly translates to increased customer loyalty and improved sales.
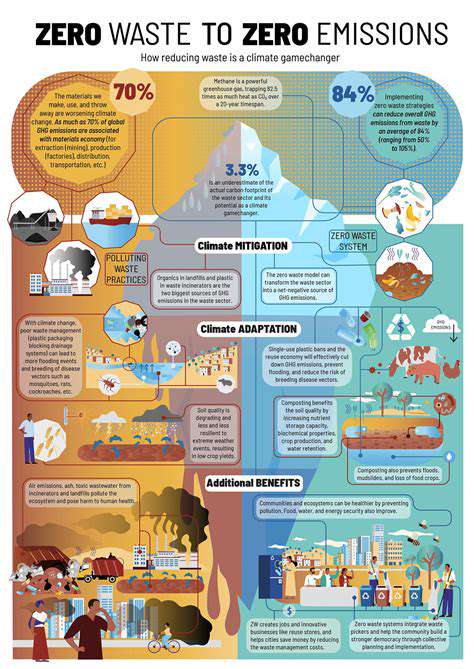
Predictive Analytics for Proactive Supply Chain Management
Understanding the Foundation
Predictive analytics, at its core, leverages historical data and statistical algorithms to forecast future outcomes. This involves analyzing patterns, trends, and relationships within the data to identify potential future events. By understanding these patterns, organizations can make more informed decisions and proactively address potential challenges.
The foundation of any successful predictive analytics implementation is a strong understanding of the data being used. This includes identifying relevant variables, assessing data quality, and ensuring data integrity. A robust data preparation process is crucial for accurate and reliable predictions.
Key Applications in Business
Predictive analytics finds wide-ranging applications across various industries. In marketing, it enables targeted campaigns and personalized customer experiences, leading to increased conversion rates and customer loyalty. In finance, it can predict potential risks and opportunities, enabling proactive risk management and investment strategies.
Furthermore, predictive analytics can be used to optimize operations, such as supply chain management, inventory control, and resource allocation. These applications lead to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved profitability.
Data Preparation and Modeling Techniques
Data preparation is paramount in predictive analytics. This involves cleaning, transforming, and preparing the data for modeling. Missing values need to be addressed, outliers identified and handled, and data normalization techniques applied to ensure optimal model performance.
Various modeling techniques are employed, including regression analysis, classification, clustering, and time series analysis. Choosing the appropriate technique depends on the specific business problem and the nature of the data. A deep understanding of these techniques is critical for achieving accurate and insightful results.
Model Evaluation and Refinement
Model evaluation is a crucial step in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of predictive analytics results. Evaluation metrics, such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, are used to assess the model's performance on unseen data. Understanding these metrics is important to identify potential biases or inaccuracies.
Refinement is often necessary to improve model performance. This involves iteratively adjusting model parameters, variables, or techniques based on the evaluation results. This iterative process ensures that the model continually evolves and provides increasingly accurate predictions.
The Role of Machine Learning
Machine learning plays a significant role in predictive analytics. Algorithms like support vector machines, decision trees, and neural networks can identify complex patterns and relationships in data that might be missed by traditional statistical methods. This allows for more accurate and nuanced predictions.
Machine learning algorithms can be used to automate the entire predictive analytics process, from data preparation to model deployment. This automation significantly improves efficiency and reduces the time required for analysis and decision-making.
Ethical Considerations and Bias Mitigation
While predictive analytics offers significant benefits, ethical considerations are paramount. Biases present in the data can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. It is crucial to identify and mitigate these biases to ensure fairness and equity in the application of predictive models.
Data privacy and security are also critical concerns. Organizations must adhere to strict data privacy regulations and ensure that models are deployed responsibly and ethically. Transparency and explainability in model outputs are also important to build trust and understand the reasoning behind predictions.
Improving Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) with External Data
Strengthening Communication Channels
Effective communication is paramount to fostering strong supplier relationships. Regular, transparent communication helps build trust and identify potential issues early on. This includes establishing clear communication protocols, such as designated contact persons and preferred methods of communication. Open dialogue about expectations, timelines, and performance metrics is vital for maintaining a collaborative environment. This proactive approach ensures that everyone is on the same page, minimizing misunderstandings and potential conflicts.
Implementing a robust communication system, such as a dedicated platform or shared document repository, can streamline information flow and improve overall efficiency. This digital approach facilitates quick responses to inquiries, reduces delays, and ensures that everyone involved has access to the most up-to-date information. By fostering a culture of open communication, both parties can anticipate and address challenges effectively, resulting in smoother operations and stronger supplier partnerships.
Evaluating and Enhancing Performance
Regular performance evaluations of suppliers are crucial for identifying areas for improvement and ensuring that they meet the required standards. This process should include a comprehensive assessment of their delivery times, quality control measures, and overall service levels. Thorough analysis of these metrics allows for targeted interventions and support to enhance supplier performance. It also provides a platform for acknowledging and rewarding their achievements, thereby fostering a positive and productive relationship.
These evaluations should also consider the supplier's ability to adapt to changing market conditions and industry best practices. By proactively identifying opportunities for improvement, businesses can help their suppliers enhance their capabilities and maintain their competitiveness. This ongoing evaluation process helps ensure that suppliers remain aligned with the business's evolving needs and goals.
Building Trust and Collaboration
Trust is the cornerstone of any successful supplier relationship. Building trust requires consistent reliability, demonstrating fairness, and transparently addressing any issues that may arise. Suppliers who are treated with respect and understanding are more likely to be committed to the long-term partnership. By consistently delivering on commitments and providing timely feedback, businesses can foster a sense of mutual respect and understanding.
Collaboration is key to achieving mutual success. Seeking input from suppliers on areas like product development, process improvements, and market trends can lead to innovative solutions and a more agile supply chain. By actively involving suppliers in the decision-making process, businesses can leverage their expertise and insights to create greater value for both parties. This collaborative approach fosters a sense of shared responsibility and a stronger, more resilient relationship.
Real-Time Monitoring and Adaptability in a Dynamic Environment
Real-Time Data Acquisition
Real-time monitoring systems rely heavily on the continuous acquisition of data from various sources. This data, often from sensors, actuators, and other connected devices, needs to be collected and processed promptly to provide actionable insights. Accurate and timely data acquisition is crucial for effective decision-making in dynamic environments. The volume of data can be substantial, requiring robust infrastructure to handle the influx and ensure reliable transmission.
The integrity of this data stream is paramount. Errors or delays in acquisition can lead to inaccurate representations of the monitored process, potentially impacting the accuracy and reliability of the overall system. Therefore, data validation and filtering mechanisms are essential to ensure high-quality inputs for subsequent analysis and decision-making.
Data Processing and Analysis
Once the data is acquired, the system needs to process it rapidly and efficiently. This stage typically involves transforming raw data into meaningful information, often through complex algorithms and statistical models. Analysis is critical for identifying trends, anomalies, and patterns in the data stream. The speed and efficiency of this processing are essential for real-time decision-making.
Sophisticated algorithms are often employed to extract valuable insights from the data. These algorithms may include machine learning models, statistical methods, or rule-based systems, depending on the specific requirements of the monitored process.
Adaptable Algorithms and Models
The core of real-time monitoring lies in the ability to adapt to changing conditions. Dynamic algorithms and models are crucial for responding effectively to unexpected events or shifts in the monitored process. This adaptability ensures that the system maintains its effectiveness even in unpredictable situations.
Adapting algorithms and models to new data patterns is essential for accurate predictions and proactive responses. Continuous learning and improvement are necessary to maintain the effectiveness of real-time systems in dynamic environments.
Alerting and Notification Systems
Real-time monitoring systems must provide clear and timely alerts about significant events or anomalies. These alerts can range from simple notifications to more complex visualizations, depending on the severity and nature of the detected issues. Effective alerting systems are essential for enabling timely intervention and preventing potential problems from escalating. These systems must be configurable to prioritize alerts and tailor notifications to specific users or roles.
Integration with Control Systems
A crucial aspect of real-time monitoring is its ability to integrate with control systems. This integration enables automated responses to detected anomalies or deviations from expected behavior. This integration is key to proactive management and control of processes. The seamless exchange of information between the monitoring system and the control system is critical for efficient and effective operations.
This integration allows for automated adjustments to parameters or actions based on real-time feedback and analysis. The degree of automation can vary, depending on the desired level of control and the complexity of the process being monitored.
Scalability and Maintainability
Real-time monitoring systems must be designed with scalability in mind. As the volume of data and the complexity of the monitored processes increase, the system needs to adapt and grow accordingly. Scalability is critical for maintaining performance and efficiency as the system evolves. Modern solutions often incorporate cloud-based architectures to support this need.
Maintaining a real-time monitoring system requires dedicated resources and procedures. Clear documentation, regular maintenance schedules, and robust support infrastructure are essential for long-term reliability and effectiveness. This ongoing maintenance ensures the system remains accurate and responsive over time.
Read more about Leveraging External Data for Supply Chain Insights
Hot Recommendations
- AI for dynamic inventory rebalancing across locations
- Visibility for Cold Chain Management: Ensuring Product Integrity
- The Impact of AR/VR in Supply Chain Training and Simulation
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Supply Chain Communication and Documentation
- Risk Assessment: AI & Data Analytics for Supply Chain Vulnerability Identification
- Digital twin for simulating environmental impacts of transportation modes
- AI Powered Autonomous Mobile Robots: Enabling Smarter Warehouses
- Personalizing Logistics: How Supply Chain Technology Enhances Customer Experience
- Computer vision for optimizing packing efficiency
- Predictive analytics: Anticipating disruptions before they hit