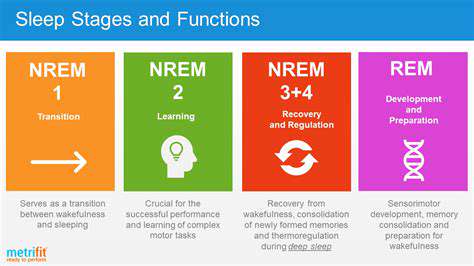
Holographic Will Creation for Digital Asset Inheritance
Navigating the Legal Landscape of Holographic Wills

Navigating the complexities of Contract Law
Contract law forms the bedrock of numerous business transactions, encompassing everything from simple agreements to intricate commercial deals. Understanding the fundamental principles of offer, acceptance, consideration, and capacity is crucial for ensuring legally sound agreements. Misunderstanding these elements can lead to costly disputes and legal battles. Moreover, contract law often involves interpreting ambiguous clauses, identifying breaches, and determining appropriate remedies.
Understanding Intellectual Property Rights
Protecting intellectual property (IP) is paramount in today's knowledge-based economy. Patents, trademarks, and copyrights safeguard creations from unauthorized use and exploitation. Understanding the nuances of each type of IP protection is essential for businesses seeking to leverage their innovative work. This involves careful documentation, registration procedures, and ongoing vigilance to maintain rights.
The Role of Tort Law in Civil Disputes
Tort law governs civil wrongs, addressing situations ranging from negligence to intentional harm. It provides a framework for individuals and entities to seek compensation for damages suffered due to another's actions or omissions. Understanding the different types of torts, such as negligence, defamation, and trespass, is essential for navigating potential legal challenges. Knowing how to demonstrate the necessary elements of a valid claim is critical.
Compliance with Regulatory Frameworks
Navigating the ever-evolving regulatory landscape is a constant challenge for businesses and individuals. Compliance with various laws and regulations, including environmental, labor, and consumer protection laws, is crucial to avoiding penalties and maintaining a positive public image. Failure to comply can result in significant financial penalties and reputational damage. Staying updated with the latest legal developments is key to maintaining compliance.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Effective dispute resolution is crucial for preventing conflicts from escalating into costly legal battles. Exploring various avenues, such as negotiation, mediation, and arbitration, can lead to more efficient and cost-effective resolutions. These alternatives to litigation can significantly reduce the time and expense associated with legal proceedings. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each method is essential for choosing the most appropriate course of action.
International Trade and Legal Considerations
International trade presents unique legal challenges, demanding a sophisticated understanding of international law and trade agreements. Navigating varying legal systems, customs regulations, and intellectual property laws across borders requires specialized expertise. International trade agreements often dictate the rules and regulations for cross-border commerce. This involves a thorough understanding of international trade law and the ability to adapt to international legal frameworks.
Employment Law and Human Resources Practices
Understanding employment law is vital for establishing fair and legally sound practices within a company. Compliance with labor laws and regulations concerning wages, working conditions, discrimination, and termination procedures is essential for mitigating legal risks. This includes ensuring appropriate documentation, adherence to legal standards, and proactive measures to prevent potential disputes. These practices are vital to maintaining a positive work environment while minimizing legal liabilities.
Beyond the Basics: Addressing Specific Digital Assets
Understanding Holographic Wills
Holographic wills, also known as home-made wills, are a unique type of will that are entirely handwritten by the testator (the person making the will). This method of will creation offers a degree of flexibility and often allows for a more personal expression of testamentary intent. However, strict legal requirements dictate the format and content needed to ensure the will's validity. Understanding these requirements is crucial to avoid potential issues down the road.
A key aspect of holographic wills is the requirement for complete handwritten creation. This includes the entire body of the will, the signature, and any necessary testamentary declarations. Any typed portions or pre-printed forms invalidate the will. This handwritten nature distinguishes holographic wills from other types of wills, like witnessed wills or those prepared by an attorney.
Legal Requirements for Validity
Specific legal requirements vary by jurisdiction, but generally, a holographic will must be entirely handwritten, dated, and signed by the testator. The signature must be located at the end of the will and must be unequivocally recognizable as the testator's signature. This requirement ensures that the will is authentic and represents the testator's true wishes.
The date of the will is equally critical. The date must be present within the will itself and clearly identifiable. The absence of a date, or a date that cannot be definitively determined, can lead to the invalidation of the will. Failure to comply with these legal requirements can lead to the will being deemed invalid and potentially result in the distribution of assets according to intestacy laws.
Compared to Other Types of Wills
Compared to witnessed wills or those prepared by attorneys, holographic wills often have a simpler process for creation. However, the inherent requirement of complete handwritten creation limits the complexity of the will. This is important to consider when dealing with complicated estates or intricate beneficiary designations. A witnessed will allows for more detailed provisions and can include complex instructions, whereas a holographic will often focuses on fundamental provisions.
Specific Considerations for Digital Assets
Digital assets, such as online accounts, cryptocurrency holdings, and intellectual property, present unique challenges and considerations for holographic will creation. These assets often fall outside the traditional scope of property covered in a will, and their handling requires specific attention. A holographic will may not adequately address the complexities associated with digital assets.
Clearly outlining how digital assets should be handled is essential. A simple statement like all my digital assets shall be transferred to my son, John Doe might be insufficient. Details on specific platforms, account login information, and other relevant details need to be included for clarity and implementation.
Potential Risks and Limitations
One potential pitfall of holographic wills is the susceptibility to errors and ambiguities. Handwritten documents can be difficult to interpret, leading to disputes among beneficiaries or with the probate court. This is a significant concern, especially when dealing with intricate or complex estate plans. The lack of professional guidance can lead to misunderstandings and legal challenges.
A significant limitation of holographic wills pertains to potential challenges in establishing authenticity and testator intent. If the will's language is ambiguous or unclear, it may be difficult for the court to interpret the testator's wishes accurately. This ambiguity can lead to protracted legal battles and delays in asset distribution. Professional legal advice is highly recommended when dealing with complex estates.
Probate Procedures and Inheritance
Probate procedures for holographic wills are generally similar to those for other types of wills. However, the lack of formality in the creation process can sometimes lead to additional complexities. The probate court will need to validate the will's authenticity and ensure it complies with legal requirements. This process can vary based on the jurisdiction and the specific circumstances of the case.
The inheritance process following a holographic will can be straightforward if the will is clear and unambiguous. However, ambiguities or challenges to the will's validity can significantly delay or complicate the distribution of assets. It is crucial to seek legal advice to ensure the smooth execution of the inheritance process.
Read more about Holographic Will Creation for Digital Asset Inheritance
Hot Recommendations
- AI for dynamic inventory rebalancing across locations
- Visibility for Cold Chain Management: Ensuring Product Integrity
- The Impact of AR/VR in Supply Chain Training and Simulation
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Supply Chain Communication and Documentation
- Risk Assessment: AI & Data Analytics for Supply Chain Vulnerability Identification
- Digital twin for simulating environmental impacts of transportation modes
- AI Powered Autonomous Mobile Robots: Enabling Smarter Warehouses
- Personalizing Logistics: How Supply Chain Technology Enhances Customer Experience
- Computer vision for optimizing packing efficiency
- Predictive analytics: Anticipating disruptions before they hit